Solid carbide flow drill, also known as friction drill,Frictiondrillng, Fdrill,chipless forming drill, flow drill, high-temperature drill, or form drill, is an innovative machining technology that originated in Europe and has been widely used in Europe and the United States for over 30 years. It overcomes the limitations of traditional drilling and fastening processes, enabling quick and easy tapping and fastening of thin sheets and tubes in just a few seconds, and has gradually replaced conventional methods such as press nuts, welded nuts, and rivet nuts.
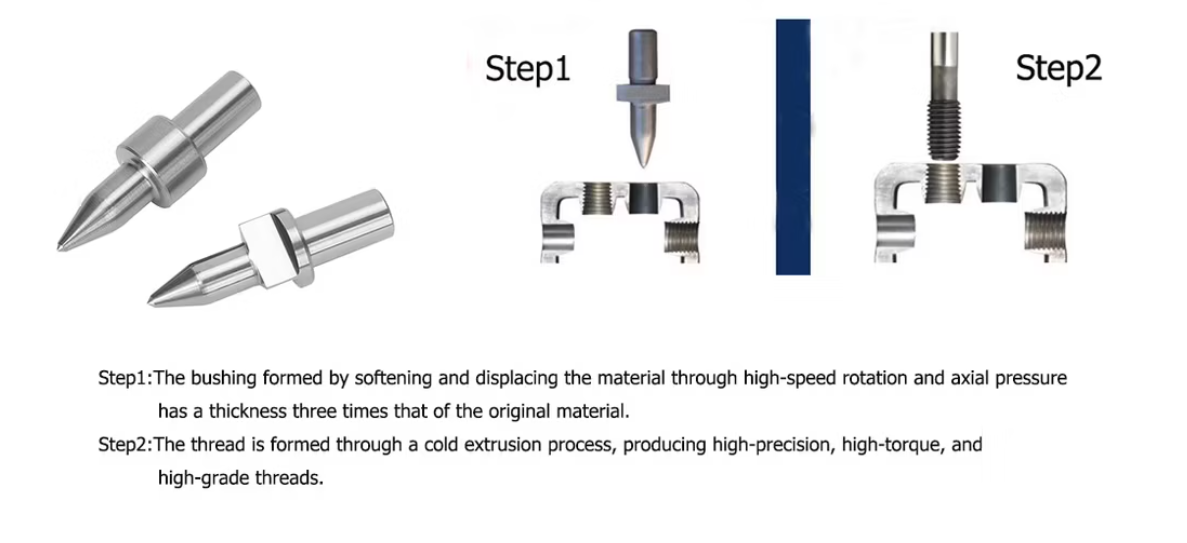
Solid carbide flow drill are made from wear-resistant, high-temperature-resistant tungsten carbide. When the high-speed rotating drill contacts the workpiece and axial pressure is applied, friction between the drill and the metal generates heat of approximately 650°C to 750°C, rapidly softening the local metal. As the drill penetrates through extrusion, it simultaneously pushes the softened metal downward to form a metal collar (bushing) with a thickness roughly three times that of the original material. The entire process takes only 3-6 seconds.
After tapping, this collar can be used directly as a nut, replacing welded nuts; it can also serve as a joint interface for brazing, welding, or copper welding. Since the process produces almost no chips and the collar is integrally formed with the base material, the resulting threads have exceptional pull-out and torsional strength. The number of engaged threads and overall strength are significantly increased, making it a complete replacement for traditional multi-step processes such as "drilling + welding.
Advantage
Compared to traditional drilling + nut installation (or welded nut) processes, thermal drilling has the following main advantages:
1. Lower Cost
In the traditional method, after drilling holes in thin sheets, you need to add and weld nuts or use rivet nuts, which increases parts and assembly costs.
Thermal drilling directly extends the hole wall into a "bushing" shape, allowing direct tapping, eliminating nut and installation costs.
2. Higher Processing Efficiency
One-pass forming, fewer steps, and shorter production cycle.
High automation potential, and can even achieve drilling + tapping in the same workstation.
3. Higher Thread Strength
The extended hole wall from thermal drilling can be 3-6 times thicker than the original sheet thickness, increasing the number of thread engagement turns, thus improving pull-out and torsional resistance.The strength can match or even exceed that of welded nuts.
4. Chip-Free Processing
Traditional drilling produces chips that require cleaning and may scratch surfaces or enter internal structures.
Thermal drilling forms holes by extrusion, producing almost no chips, keeping the workspace cleaner and reducing cleanup time.
5. Wide Material Applicability
Can be used for most metal sheets such as steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and copper.
Suitable for sheet or tube materials with thickness from approx. 0.5 mm to 12 mm.
6. Good Appearance and Precision
Smooth, neat hole edges with dense inner walls and no burrs.
Avoids deformation and weld marks that welded nuts may cause.
Specification
The standard diameter range of Friction drill thermal drilling bits is from 2.0 mm to 25.4 mm.
The specifications and sizes of Friction thermal drills are generally classified according to thread types, with common specifications including:
Metric Coarse/Fine Threads (M): M3, M4, M5, M6, M8, M10, M12, M14, M16, M18, M20
British Standard Pipe Parallel Threads (BSP): G1/8, G1/4, G3/8, G1/2, G3/4
Unified National Coarse/Fine Threads (UNC/UNF): No.4, No.5, No.6, No.8, No.10, No.12, 1/4, 5/16, 3/8, 7/16, 1/2, 9/16, 5/8, 3/4
National Pipe Taper Threads (NPT): 1/8", 1/4", 3/8", 1/2", 3/4"
Special-size Friction drill thermal drilling bits can be custom-made according to user requirements.
Our technical support team will design and manufacture special-size Friction drill bits based on the customer's machining needs and will also provide testing and analysis services upon request.
Classification of Thermal Drills:
According to the surface requirements of the workpiece, Friction Drill thermal drill bits are divided into Standard Thermal Drill (Round Mouth Type) and Flat Mouth Thermal Drill (Planing Type):
Standard Thermal Drill (Round Mouth Type):
When the thermal drill penetrates the workpiece and forms the extended bushing, it simultaneously creates a raised ring on the surface. This raised collar is suitable for thread sealing or for use with a nut washer.
Flat Mouth Thermal Drill (Planing Type):
The stepped middle section of the thermal drill is ground with milling edges. While penetrating the workpiece and forming the extended bushing, it also cuts off the raised ring on the surface (milling it flat and chamfering it), resulting in a smooth workpiece surface.

According to the workpiece thickness, Fdrill thermal drilling tools are divided into short drills and long drills.
Short drill: Used for common thin-walled parts. Suitable for penetrating workpieces with a thickness of 0.8 mm-3 mm. The cylindrical part of the drill bit is relatively short. After extrusion forming, the resulting hole is conical, which helps enhance thread strength.
Long drill: Used for thicker workpieces or situations where a straight hole is required. Suitable for penetrating workpieces with a thickness greater than 3 mm-12 mm. The cylindrical part of the drill bit is longer, and after extrusion forming, the resulting hole is longer.
E-mail: sales@ztcarbide.com
Add: No.1 of Longxin international building, No.255 of Tongxia Road,Shi Feng District, Zhuzhou Hunan Province,China
We chat